3.Cubic boron nitride (CBN) grinding wheel selection
Which types of grinding wheel should I choose?
There are many types of grinding wheels with various shapes and sizes. Each grinding wheel has a certain range of application according to the abrasive material, the bonding material, and manufacturing process of the grinding wheels. If improperly selected, it will directly affect the processing accuracy, surface roughness, and production efficiency. Therefore, when grinding, should choose the appropriate grinding wheel according to the specific situation. So you need to know the tips of grinding wheel selection
1. Conventional grinding wheel selection
1)The most commonly used abrasive is brown fused alumina(A) and white fused alumina(WA), followed by black silicon carbide(C) and green silicon carbide(GC). The rest are pink fused alumina(PA), monocrystalline fused alumina(SA), microcrystalline fused alumina(MA), fused zirconia alumina(ZA).
Brown fused alumina grinding wheel: Brown fused alumina has high hardness and high toughness, which is suitable for grinding metals with high tensile strength such as carbon steel, alloy steel, malleable cast iron, hard bronze, etc. This kind of abrasive has good grinding performance and wide adaptability.
White fused alumina grinding wheel: The hardness of white fused alumina is slightly higher than that of brown fused alumina, and the toughness is lower than that of brown fused alumina. When grinding, the abrasive grains are easily broken. Therefore, the grinding heat is small, and it is suitable for manufacturing the grinding wheel for fine-hardened steel, high carbon steel, high-speed steel and grinding thin-walled parts. The cost is higher than that of brown fused alumina.

Black silicon carbide grinding wheel: Black silicon carbide is brittle and sharp, and its hardness is higher than that of white fused alumina. It is suitable for grinding materials with low mechanical strength such as cast iron, brass, aluminum, and refractory materials.
Green silicon carbide grinding wheel: The hardness and brittleness of green silicon carbide are higher than that of black silicon carbide, and the grains are sharp and it has good thermal conductivity. It is suitable for grinding hard and brittle materials such as tungsten carbide, optical glass, and ceramics.
Pink fused alumina grinding wheel: It is suitable for grinding tools, measuring tools, instruments, threads and other workpieces with high surface quality requirements.
Monocrystalline fused alumina grinding wheel: It is suitable for grinding stainless steel, high vanadium high-speed steel and other workpieces with high toughness, high hardness, and easily deformed burns.

Microcrystalline fused alumina grinding wheel: It is suitable for grinding stainless, bearing steel and special ductile iron, etc. It is used for forming grinding, cut-in grinding, and mirror grinding.
Fused zirconia alumina grinding wheel: It is suitable for grinding austenite, titanium alloy, heat resistant alloy, especially suitable for heavy load grinding.
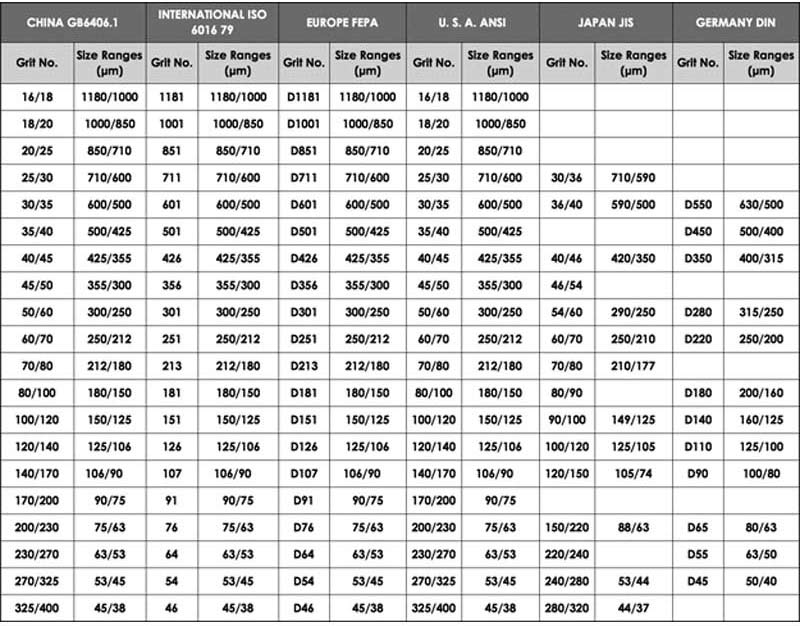
(2).The selection of grain size depends mainly on the surface roughness and grinding efficiency of the workpiece being ground.
Grain size refers to the grain size of the abrasive and its size is indicated by the grain size number. When grinding with coarse-grained grinding wheels, the production efficiency is high, but the surface of the ground workpiece is rough. When grinding with the fine-grained grinding wheel, the surface of the ground workpiece is better, and the productivity is lower. Under the premise of meeting the roughness requirements, coarse-grained grinding wheels should be used as much as possible to ensure high grinding efficiency. Usually, the coarse-grained grinding wheel is used for rough grinding, and the fine-grained grinding wheel is used for fine grinding.
When the contact area between the grinding wheel and the workpiece is large, should choose the coarser grain size grinding wheel. For example, when grinding the same plane, the grain size for grinding the end face is coarser than for grinding the periphery.

(3)The selection of hardness depends mainly on the workpiece material being ground, grinding efficiency and the quality of the machined surface.
Hardness refers to the difficulty of the abrasive wheel falling off under the action of external force. To meet the requirements of different workpiece material grinding, the grinding wheel is divided into different hardness grades.
If the grinding wheel is hard, the abrasive grains are not easy to fall off, and the grinding wheel blocks easily and the grinding heat is increased, and easily burns the workpiece, and the grinding efficiency is low, affecting the surface quality of the workpiece. If the grinding wheel is too soft, the abrasive grains are also off when it is sharp, and it increases the wear of the grinding wheel, easily loses the correct geometry and affects the workpiece accuracy.
Therefore, should choose the right hardness of grinding wheel. It should also be considered according to the contact area of the grinding wheel and the workpiece, the shape of the workpiece, grinding way, cooling method, bond type of the grinding wheel and other factors.
![]()
The hardness selection principles of grinding wheel are for reference as follows:
- When grinding soft materials, choose the harder grinding wheels. When grinding hard materials, choose the soft grinding wheel.
- When grinding soft and tough non-ferrous metals, choose the softer hardness.
- When grinding poor thermal conductivity materials, choose the grinding wheels with softer hardness.
- The hardness of the grinding wheel for end face grinding is softer than that of periphery grinding.
- Under the same grinding conditions, the hardness of the resin bond grinding wheel is 1-2 grade higher than that of vitrified bond grinding wheel.
- When the rotation speed of the grinding wheel is high, choose the soft 1-2 grade of the hardness of the grinding wheel.
- The hardness of grinding wheel with coolant grinding is 1-2 grade higher than the grinding wheel for dry grinding.
(4) The selection of bond should be considered in terms of grinding methods, speed of use and surface processing requirements.
There are vitrified bond (V) and resin bond(B).
The vitrified bond is an inorganic bonding agent with stable chemical performance, good heat resistance, good corrosion resistance, and high porosity. This wheel has high grinding efficiency and low wear, and can better maintain the geometry of the grinding wheel, and the application is wide. It is suitable for conventional carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, cast iron, tungsten carbide, non-ferrous metals, etc. But, the vitrified bond grinding wheel is relatively brittle and cannot be subjected to severe vibration. Usually, only the grinding wheel is used at the speed of 35m/s below.
The resin bond is an organic bond agent, and resin bond grinding wheel has high strength, certain elasticity, low heat resistance, good self-sharpness, simple production and short cycle time of the process. The resin bonded can be manufactured the grinding wheels with working speed higher than 50m/s and very thin grinding wheels. Its application range is second only to the vitrified bonding agent.
It is widely used for rough grinding, snagging, cutting off and free grinding such as grinding steel ingots, casting burrs, etc. It can manufacture the grinding wheel with high speed and high glosses, heavy load, cutting off and other special requirements.

(5) The selection of structure mainly should be considered the pressure, grinding method, and workpiece materials.
The structure refers to the percentage of the grinding wheel volume occupied by the abrasive grains in the grinding wheel. The grinding wheel is graded at the percentage of 62% of the abrasive grain volume as 0 # number organization. The volume of the abrasive grain is reduced by 2%, the tissue is increased by 1#, which is divided into 15 numbers. The larger the number, the looser the structure is.
The grinding wheel with compact structure can grind the better surface of the workpiece. The grinding wheel with loose structure can ensure the holding the grinding debris and avoid the blockage of the grinding wheel due to the large gap. When rough grinding and grinding softer metals, the grinding wheel easily blocks and should choose the grinding wheel with a loose structure.
When forming grinding and precision grinding, should choose the grinding wheel with a compact structure to maintain the geometry of the grinding wheel and obtain better roughness. When grinding the machine tool guide rail and tungsten carbide tools should choose the grinding wheel with a loose structure to reduce the thermal deformation of the workpiece and avoid burn and cracks. When grinding the heat-sensitive materials, non-ferrous metals and non-metallic materials should use more than 12# structure grinding wheels.
(6) The shape and size should be selected according to the conditions of the grinding machine and the shape of the workpiece.
There are plane grinding wheels(P), wheels recessed one side(PDA), wheels recessed two sides (PSA), thin grinding wheels(PB), cylindrical grinding wheels(N), bowl-shaped grinding wheels(BW), dish-shaped 1# grinding wheels(D1), etc.
The shape and size of the grinding wheel that can be used in every type of grinding machine have a certain range. The outer diameter of the grinding wheel should be chosen as large as possible to increase the linear velocity of the grinding wheel, obtain higher productivity and surface quality of the workpiece, and the same effect can be obtained by increasing the width of the grinding wheel.

2.Diamond grinding wheel selection
Compared with the grinding wheel made from conventional abrasive grains such as boron carbide, silicon carbide, and fused alumina, the diamond grinding wheel have sharper edges, low wear, long life, high productivity, and good processing quality, but the price is expensive. They are suitable for finish grinding high hardness, brittle and difficult-to-machine materials such as tungsten carbide, ceramic, and semiconductor.
The features of the diamond grinding wheel include the type of abrasive, grain size, hardness, concentration, bond, shape, and size of the grinding wheel.
Abrasives: Synthetic diamond (JR) is widely used according to its crystal shape and particle strength. It can be divided into various models according to the application.
Grain size: Consider three aspects of workpiece roughness, grinding productivity and diamond consumption.
Hardness: Only the resin bond diamond grinding wheel has the features of “ hardness”. S(Y1) grade or higher is used.
Bond: There are resin bond, vitrified bond, bronze bond, and electroplated metal bond.

The resin bond diamond grinding wheel has high grinding efficiency, good roughness of the workpiece to be processed, wide application range, good self-sharpness, not block easily, low heat, easy dressing, and poor wear resistance, mainly used in the finish grinding.
The vitrified bond diamond grinding wheel has good self-sharpness and sharp grinding. It is mainly used for grinding various non-metallic hard and brittle materials such as tungsten carbide, PCD, PCBN, industrial ceramics, etc.
Bronze bond has good wear resistance, but it is not easy for dressing. It is mainly used for processing automotive glass, magnetic materials, optical glass, and other products.
The electroplated diamond grinding wheel is sharp and can be made into various shapes, but the life is short and can be applied to various kinds of hard materials.
Concentration: The selection of concentration depends on the grain size, bond, shape, processing method, production efficiency and wheel life requirements of the grinding wheel. The diamond grinding wheel with high concentration has a strong ability to maintain the shape of the grinding wheel. When grinding wheel with low concentration grinding, diamond consumption is often lower and should be selected as needed.
Shape and size: selected upon the shape and size of the workpiece and conditions of the machine tool.

3.Cubic boron nitride (CBN) grinding wheel selection
The cubic boron nitride (CBN) grinding wheel is most suitable for processing hard-to-machine steel with high hardness, high viscosity, high-temperature strength, and low thermal conductivity, and high speed or ultra high speed grinding. Its application range complements synthetic diamond.
Diamond wheels have a unique effect when grinding tungsten carbide and non-metallic materials, but the effect is not significant when grinding steel, especially when grinding special steel. The efficiency of grinding cubic steel by CBN grinding wheel is nearly 100 times higher than that of fused alumina grinding wheel, and it is 5 times higher than that of the diamond grinding wheel, but grinding brittle material is not as good as the diamond.
The selection of a CBN grinding wheel is similar to that of the diamond grinding wheel. Vitrified bond CBN grinding wheel is an important development product, mainly used for grinding difficult-to-machine ferrous metals such as titanium alloy, high-speed steel and malleable cast iron.
The resin bond CBN grinding wheel suitable for grinding ferromagnetic materials and is an ideal for processing steel. The concentration of the CBN wheel is usually between 100% and 150%. It is economical and reasonable. It can not use conventional cutting fluid and requires special cutting fluid.

4.Selection of grinding wheel with big pores
The grinding wheel with big pores features is to be blocked, high durability and strong cutting ability when grinding. It is suitable for rough and finishes grinding of non-metallic materials such as soft metals and plastics, rubber and leather. At the same time, it features fast heat dissipation, so it has a good effect in grinding some heat-sensitive materials, thin-walled workpiece and dry grinding processes( such as sharpening tungsten carbide tools and machine tool guide rails).
The manufacturing method of grinding wheel with big pores is the same as that of the conventional vitrified bond grinding wheel. The difference is that adding a certain amount of porogen into the furnish, which is completely volatilized or burned before the grinding wheel is sintered, thereby there are some pores.
The product range of grinding wheel with big pores: The abrasives usually are carbide and fused alumina, such as black silicon carbide(C), green silicon carbide(GC) and white fused alumina(WA), which have high hardness, brittle, sharp with good thermal and electrical conductivity. The abrasive grain size(36#-180#), bond(vitrified), hardness(G-M grade), shape( flat, cup, bowl or dish), pore size( about 0.7-1.4mm)
Conclusion:
We should know the right grinding wheel selection according to the actual situation in practical applications.
Remarks: Click on the text below to learn about the most comprehensive knowledge of diamond and CBN grinding wheels.
.webp)